You might think of object recognition software in the context of computer-aided design as a key component of the process that enables projects to transfer images from one file format to another. It is especially useful when creating a vector since it allows for a level of precision that increases the likelihood that complex raster components will be converted to the appropriate vector components.
Visual object recognition is a computational issue that is extremely challenging. The major issue is that everything on Earth has the potential to project an infinite number of different 2-D images onto the retina when its position, posture, lighting, and background change in relation to the spectator. However, this issue is simply resolved by the mind. The creation of artificial recognition systems that finally mimic our very own visual talents, frequently with biological inspiration, is necessary for progress in our understanding of how the mind resolves the problem of object recognition.
As AI becomes more prevalent, machines may now be programmed to comprehend the things they observe. Automation has been helped by computer vision, and more specifically, object identification algorithms, in a variety of industries. The advancements made in the assembling industry as a result of these new capabilities are enormous. However, for computer vision developers, object recognition will frequently be a more difficult procedure and assignment to complete.
Functions of Object Recognition Software
When someone is familiar with something’s past and understands it, they feel recognised. This may be because the subject being discussed has already been presented to us in a plain manner or because we are familiar with comparable things that have similar characteristics. Computers are prepared to perform object recognition because of this process.
Naturally, there are a variety of methods to approach this issue. Different models are created depending on factors like the difficulty of the subject matter, the amount of time allotted for the activity, or the degree of precision required for the recognition. Programming software engineers should also illustrate how problems with lighting, shifting camera angles, and obstructions from things might make it difficult to recognise items.
Let’s examine two of the main production processes for object identification software. Keep in mind that some businesses will combine the two techniques.
Machine Learning
To identify the explicit properties of the objects, this framework first examines images and recordings. Manual component extraction is what we call it.
The identified features then need to be organised into classes.
Machines have a huge capacity for knowledge acquisition and self-learning. They can also modify recently prepared data while changing calculations.
In-depth Learning
Deep Learning follows a completely different philosophy. Deep neural networks must handle enormous numbers of objects in order to function at the level of raw information.
They automatically learn to follow the differences and similarities between items.
An early application of deep learning is Google Brain. After appearing in over ten million images, it has found out how to find cats in.
As a result, deep learning networks shouldn’t use altered characterization criteria. They learn how to perceive questions by having access to vast amounts of information.
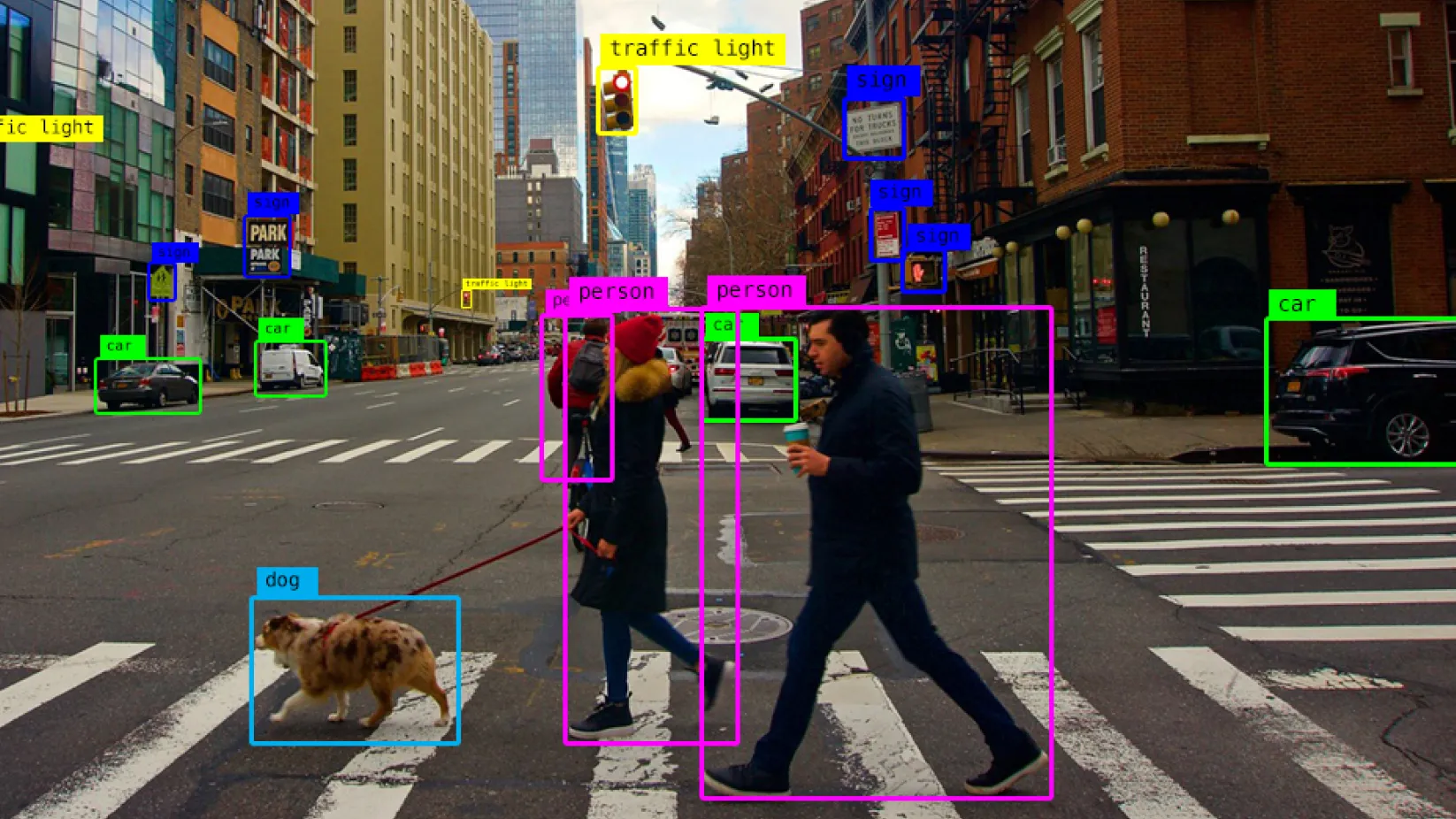
Healthcare’s Major Practical Cases for Object Recognition
By helping clinicians identify diseases from HD photographs, MRIs, and CT scans, object identification, particularly its deep learning-based kind, may be able to save lives.
Medication is a rare topic where efficient and labelled picture collections already exist, speeding up and simplifying the building of deep learning models.
Manufacturing
This concept has the potential to become an amazing resource for production.
Modern robots are capable of following all protocols, and providing them object recognition capabilities helps to identify human error.
The increased productivity this software provides might assist businesses in optimising process automation and elevating quality control.
Defense and security
The security and defense industries are two areas where object recognition is used pretty openly outside of the CAD community. Since necessary CCTV was established around the country, video monitoring has advanced significantly. Presently, cameras are able to track, identify, and detect moving things due to complex usage of object recognition software.
Management of content
Media companies have successfully coupled object recognition as a technique for automating content association with their vast databases of images and recordings. Object identification is also connected to faster content recovery and better compliance.
Automotive
The auto industry has benefited greatly from the integration of object recognition, especially as it progresses towards the development of driverless cars.
In order for a vehicle to identify and respond to changing street signs, street markings, pedestrians, and other cars without human intervention, object recognition is essential.
Volvo even uses the data it gathers with the help of object recognition to plan when to replace spare components or service the car.
Object recognition is a fantastic tool that may be used for a huge variety of different purposes, as should be evident. Whatever your line of work, you can probably find a method to include a product form into a task! You could even create your own object recognition software if you’re so inclined. You can only achieve it thanks to initiatives like MATLAB!
The requirement for software testing remains constant despite the fact that technologies change so rapidly because every software product must be tested before it is released to the market in order to be valuable. So come to us right away for all of your software testing requirements, and we’ll meet them as soon as you provide the products.





Recent Comments